Abstract:
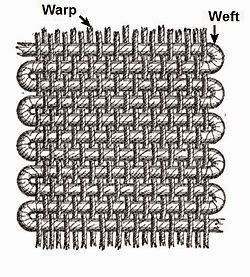
In this experiment the bending length of the cotton woven fabric has been determined. The bending length is very important factor which determines the flexibility of the fabric. The bending length in both the warp and weft direction of the fabric is important in calculating the flexibility of the fabric. The warp and weft-wise bending length hence determined in this experiment and results has been discussed.